What Are Nerve Cells?
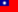
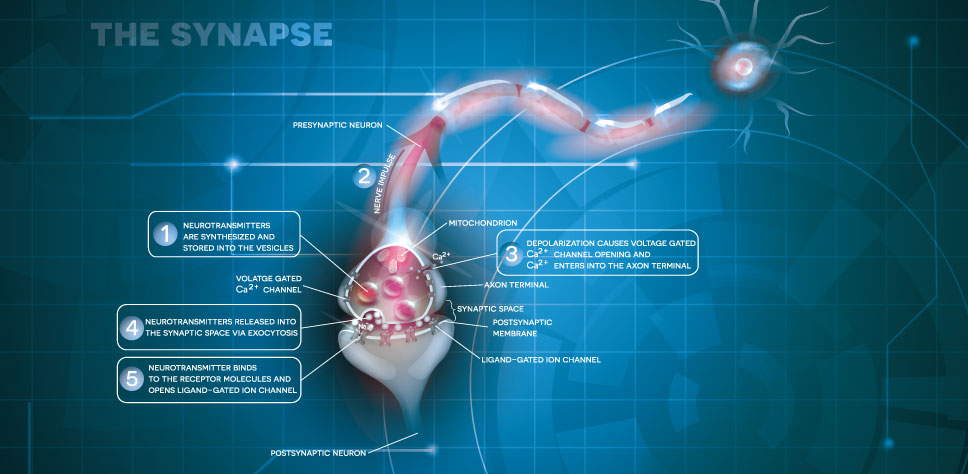
At a cellular level, the nervous system mainly contains two types of cells, neurons and neuroglial cells. Neurons make up nerve tissue and form part of the structure and function of the nervous system. Neurons provide special functions such as thinking, controlling muscle activity, and regulating glands. Neuroglial cells are a special protective component of the nervous system.
| Neurons | Neuroglial cells | |
|---|---|---|
| Character | Be able to perceive changes in the environment, then pass the information to other neurons and instruct collective reactions. | Performing support and protection functions, some neuroglial cells can participate in the transmission of messages. |
| Volume | Large | Small |
| Quantity | Small | Large |